Abstract:
While large companies have the capability and resources to protect their systems from the increasing number of cyberattacks, little is known regarding the recent cybersecurity preparedness of Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs). The purpose of this study is to examine the factors that impact the SMB's readiness towards cyberattacks, this research used the identified constructs, the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks, government regulations and support, cyberattacks, awareness of cybersecurity-threat, and information technology risk management that were established in prior research. The findings demonstrated an overall good model. In addition, the results showed that government regulations and support, awareness of cybersecurity-Threat, and information technology risk management have a significant impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack. Furthermore, government regulations and support have a significant impact on cyberattacks and awareness of cybersecurity-threat. These findings can be used to facilitate future studies and improve the existing understanding of how SMBs can be prepared to reduce the incidence and effect of cyberattacks.
Key Words:
Awareness of Cybersecurity, Cyberattacks, Readiness, SMB
JEL Classification:
Introduction
COVID-19 has a remarkable effect on the world, business operations, and individuals. The increase usage of technology in a daily basis for individual and business is an indication of the digital development and expansion. (Mckinsey, 2020). Businesses encountered overwhelming adjustments in conducting their activities, thus, in a short period of time they implemented digital solutions to overcome this situation and to continue working from home (Amankwah-Amoah, Khan, Wood, & Knight, 2021). However, while working on distance can help organizations to continue operating, this situation increases the risk of threats, and companies may suffer a financial loss as a result of a cyberattack or data breach (Alharbi, Alsulami, Al-Solami, Al-Otaibi, Al-Osimi,
Al-Qanor, & Al-Otaibi, 2021).
While large companies have the capability and resources to protect their systems from the increasing number of cyberattacks, little is known regarding the recent cybersecurity preparedness of SMBs (Bada & Nurse, 2019). Cyberattack has been defined as "a cyber operation conducted to alter, disrupt, deceive, degrade, or destroy computer systems or networks or the information and/or programs resident in or transiting these systems or networks (Russel, 2014, p.8)." SMBs who are considered not capable enough to cope cyberattack are facing a major disruption and loss. In most instances, the owner of SMBs do not have a strategy or resources to develop their cybersecurity plan because they did not understand the risk that may impact their company’s survival (Alharbi et al. 2021; Bada & Nurse, 2019; Berry & Berry, 2018).
SMBs with less than 250 full-time employees are considered the majority of businesses in the world and have an essential part in economic growth (Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021). SMBs are depending on digital technology for their day-to-day tasks. However, SMBs are likely to be more vulnerable to cyberattacks due to the increase in the interconnection of digital devices expedited by the Covid-19 pandemic (Perozzo, Zaghloul, & Ravarini, 2022) and the lack of enough resources (Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021). Lewis (2020) stated that there are signs indicating that SMBs are facing continuous cyberattacks from Hackers.
In the case of Saudi Arabia, 99% of all organizations are noted as SMBs, with nearly 28.75% of the total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and 43.61% of the GDP for the non-oil sector (Monshaat, 2022), which indicates that SMB's are the majority of businesses in Saudi Arabia. These figures reveal the significance of SMBs to the Saudi Arabia economy’s stability and growth. However, there is a limited number of studies measuring cyberattack readiness at SMBs in Saudi Arabia.
Prior researchers such as Hasan, Kurnia, and Thurasamy (2021) examined the factors affecting the organization's cyberattack readiness and the impact of these factors on organizational performance. Also, Berry & Berry (2018) interviewed the owners of SMBs to assess their risk management plan for cyberattacks. Alharbi et al. (2021) measured the efficiency of security practices at SMBs in Saudi Arabia, however, the study did not investigate the readiness of these enterprises for cyberattacks. In addition, Perozzo, Zaghloul, and Ravarini (2022) proposed a CyberSecurity Model for small and medium enterprises based on a Socio-Technical view of organizations. The study, though, investigates three manufacturing businesses that lack the generalizability of the results.
Alahmari and Duncan (2020) revealed in their systematic review of cybersecurity risk management in SMBs that threat, behavior, practice, awareness, and decision-making explain the significance of the leadership part for the constancy of SMBs in the cybersecurity field. Nevertheless, most of the studies investigated SMBs in developed countries such as the United Kingdom and the United States (Alahmari & Duncan, 2020). Furthermore, Renaud and Ophoff (2021) stated that SMBs' lack of cyberattack readiness needs more attention from researchers. In addition, Hasan et al. (2021) indicated that investigating the impact of government support on cyberattack readiness is warranted. Chidukwani, Zander, and Koutsakis (2022) found that researchers in SMB cyberattacks is mainly focusing on qualitative studies and argued that " SMBs should have the ability to detect, respond and recover from cyber-attacks, and if research lacks in those areas, then SMBs may have little guidance on how to act" (p. 85701).
To address this research gap, this study aims to empirically assess SMBs' readiness toward cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia. Thus, this research have the following questions:
To what extent do Cyberattacks impact the SMB's Readiness towards Cyberattacks.
To what extent does Awareness of Cyberattacks impact the SMB's Readiness towards Cyberattacks.
To what extent does Information Technology Risk Management impact the SMB's Readiness towards Cyberattacks.
To what extent do Government Regulations & Support impact the SMB's Readiness towards Cyberattacks.
Theoretical Background Small and Medium Business & Cyberattacks (CT)
SMBs are the most exposed to cyberattacks because they are less likely to have a reliable cybersecurity readiness strategy (Hiscox, 2017). Prior studies revealed that SMBs continue to be vulnerable to cyberattacks because they do not have an actionable plan to secure their systems and data (Ncubukezi, Mwansa, & Rocaries, 2020; Renaud & Ophoff, 2021). SMBs face the risk of becoming the target of cyberattacks if they disregard cybersecurity (Muncaster, 2020). However, studies indicated that SMBs didn't see themselves as favorable targets for a cyberattack because they are small (Renaud & Ophoff, 2021; Teufel, Teufel, Aldabbas, & Nguyen, 2020). In addition, cybersecurity specialists and IS researchers have indicated that SMB systems and data are in great danger due to the owners' lack of knowledge about cyberattacks (Osborn and Simpson, 2018). Eilts (2020) found that the common cyberattacks that bring about severe financial outcomes to SMBs are phishing/social engineering, web-based attacks, malware, stolen devices, and denial of service attacks.
Researchers in the IS field argued that there is
not a sufficient guidance for SMB owners to reach good decisions about diminishing and/or preventing cyberattacks (Gafni & Pavel, 2019). Eilts (2020) revealed that it is challenging for SMB owners to measure their cybersecurity status without establishing cyberattack preparedness activities. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H1: cyberattacks will have a negative impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks.
Information Technology Risk Management (ITRM)
According to Paulsen and Toth (2016),
"Cybersecurity risk management is the process of evaluating business operations and planning risk-related activities including assessing risk, responding to a risk once determined, and monitoring risk over time." In the IS literature, various methods of risk management have been created and assessed. Rohn, Sabari, and Leshem (2016) assessed the COBIT model implemented for SMBs and observed that they are vulnerable to cyberattacks due to the lack of cybersecurity awareness and owners' obligation to diminish cyber threats. Berry and Berry (2018) assessed small businesses’ cyber risk management instruments and techniques. However, this evaluation concentrating on password usage and performing the business cybersecurity protocols and policies that were established by the business. Other concepts related to cyber threat include the systematic identification and documentation of risks, the classification of these risks, the determination of an acceptable threshold for risk, and the advancement of threats mitigation practices (Carías, Arrizabalaga, Labaka, & Hernantes 2021; Cybersecurity, 2018; Estay, Sahay, Barfod, and Jensen, 2020; Gourisetti, Mix, Mylrea, Bonebrake, & Touhiduzzaman, 2019).
Chidukwani, Zander, and Koutsakis (2022) conducted a study to understand the major challenges SMBs face in applying a good cybersecurity plan and argued that more research is warranted to understand the risk management methods that SMBs carry out to prevent or mitigate cyberattacks. Alahmari and Duncan (2020) revealed in their systematic review of Cybersecurity risk management in SMBs that most of the studies assessed SMBs in developed countries such as the United Kingdom and the United States, thus, they argued for more empirical researches in the field of cybersecurity risk management, mainly in developing countries. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H2: Information Technology Risk Management will have a positive impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack.
Awareness of Cybersecurity Threats (ACT)
A crucial part of a business's cybersecurity strategy is developing awareness about the cyberattack and how to safeguard its systems and data (Bada & Nurse, 2019). Shaw, Chen, Harris, and Huang (2009) defined cybersecurity awareness as “The degree of understanding of users about the importance of information security and their responsibilities and acts to exercise sufficient levels of information security control to protect the organization’s data and networks” (p. 93). Cybersecurity awareness is an essential factor for SMBs to survive in today’s digital environment (Perozzo et al., 2022). Therefore, as a consequence of their limited awareness of cyberattacks, they rarely conduct cyberattack evaluation which indicates low cybersecurity readiness (Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021)
SMBs are struggling in conforming to new regulations and implementing security procedures in their systems due to a absence of awareness and experience (Bada & Nurse, 2019). In the context of Saudi Arabia, A report showed that 93% of SMBs experienced cyberattack incidents that resulted in a financial loss (Monshaat B, 2021). The prior research provides various frameworks and programs to support SMBs towards the cyberattack, however, this may necessitate that the SMBs owners have the knowledge to select the appropriate frameworks and programs, which are rarely that SMBs' owners have (Perozzo et al., 2022).
Chizanga, Agola, and Rodrigues (2022) stated that the lack of cyberattack awareness, cybersecurity training, and regulations are the key aspects influencing cyberattack readiness. Alahmari and Duncan (2020) indicated that threat, behavior, awareness, and owners' decision clarify the implication of the managing style for the constancy of SMBs toward cybersecurity, however, most studies investigated SMBs in developed countries. Moreover, governments and educational institutions should encourage researchers to conduct more studies into SMB cyberattacks (Chidukwani et al., 2022). Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H3: Awareness of cybersecurity threats will have a positive impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack.
Government Regulations and Support (GRS)
The use of the Internet and digital devices is expanding in all types of businesses. Governments are concerned about threats that occur from this expansion (Syafrizal, 2020). Government regulations and support are considered as a major role in confirming organizational readiness to prevent cyberattacks by establishing cybersecurity awareness (Hasan et al., 2021). According to Kiganda (2022), "Regulations are the rules, laws, and policies that the government passes to control how businesses behave and operate. (p. 9)" Furthermore, governments are taking the responsibility of creating the guidelines and policies to develop common practices across industries toward cyberattacks (Kiganda, 2022). As result, governments and private entities have suggested programs to offer information and guidance for SMBs' cybersecurity to enhance their awareness. Such as the Cyber Essentials scheme in the UK and the Information Assurance Standard in the USA. Furthermore, they provide free training programs to educate business owners about cyberattacks and protecting their assets. According to Lee & Shin (2018), a business that did not meet regulatory constraints may face criminal fines.
However, Renaud and Wier (2016) found that there is a large amount of information on the Internet which is conflicting in many situations, therefore, causing misleading and uncertainty amongst SMBs. These findings go in line with the results of (Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021) who assess how SMBs’ cyber situational awareness impacts the execution of cybersecurity practices and found that 56% of participants agreed the information available is overwhelming, thus, 55% of participants have a hard time to follow all the pieces of advice regarding cyberattacks.
Sia, Hosseinian-Far, and Toe (2021) conducted a study to identify the cause of poor cybersecurity readiness at small businesses in Singapore and found that government and academic institutions can play an essential part to improve awareness of cyberattacks. The study stated that to better understand the low level of cyberattack readiness, more studies are needed in other countries with different sizes of organizations. In addition, Noparumpa, Ruangkanjanases, and Hariguna (2021) investigated a variety of factors that affect cybersecurity readiness in organizations including technology and environment, and asserted that other factors should be examined such as government support and regulations.
H4: Government regulations and support will have a positive impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack.
H5: Government regulations and support will have a positive impact on cybersecurity awareness.
H6: Government regulations and support will have a negative impact on cyberattacks
Research Model
To examine the factors that impact the SMB's readiness towards cyberattacks, this research used the identified constructs the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks, government regulations and support, cyberattacks, awareness of cybersecurity-Threat, and information technology risk management that were established in prior research (Alharbi et al. 2021; Berry & Berry, 2018; Eilts, 2020; Erendor & Yildirim, 2022; Hasan et al., 2021; Kiganda, 2022; Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021) (see Fig. 1). Based on the literature analysis, cyberattacks measures were adopted from (Alharbi et al. 2021; Berry & Berry, 2018; Eilts, 2020), information technology risk management measures were adopted from (Alharbi et al. 2021; Berry & Berry, 2018; Kiganda, 2022), cybersecurity awareness measures were adopted from (Eilts, 2020; Erendor & Yildirim, 2022), government regulations and support measures were adopted from (Hasan et al., 2021; Kiganda, 2022), and the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack measures were adopted from (Hasan et al., 2021).
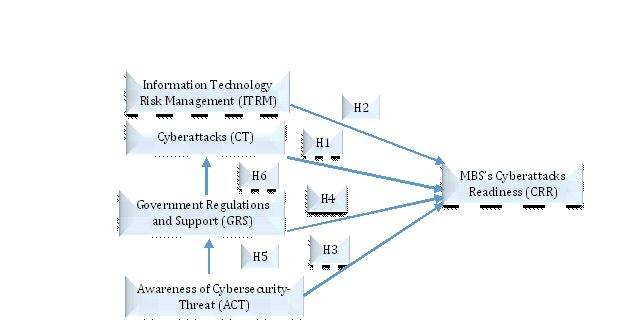
Research Methodology
The research employed a quantitative research method to empirically examine how government regulations and support, cyberattacks, cybersecurity awareness, and information technology risk management influence the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks in the context of Saudi Arabia. The survey items were adopted from preceding literature research (Alharbi et al. 2021 Berry & Berry, 2018; Eilts, 2020; Erendor & Yildirim, 2022; Hasan et al., 2021; Kiganda, 2022; Renaud, & Ophoff, 2021). The study used a five-point Likert-type scale. In addition, the study used the pre-test tool to conduct a test on a sample of 5 specialized professors in the field of information systems and analyzed the answers that were acquired. Then, the researcher sent the survey to the MSBs' participants via an internet-based delivery of the instrument were used (Google Forms) to collect the data. Next, data-checking process were conducted to confirm the analysis reliability and validity, and used different measures to find missing data and biases responses. Thus, 8 responses were removed and 207 responses were carried out to conduct the analysis. Then, the PLS method were used to analyze the data. Table 1 shows descriptive and demographic statistics for the study participants.
Table 1 Demographics Statistics (N = 207).
|
Item |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
|
Gender Male Female |
99 108 |
48 52 |
|
Age Under 20 20 – 30 31 –
40 41 – 50 Older than 50 |
9 115 60 19 4 |
4.4 55.55 29 9.2 1.9 |
|
Education High School or less Diploma Bachelor Master Doctorate |
42 24 122 14 5 |
20.3 11.59 58.95 6.76 2.4 |
|
The number of years you have worked in your
current job Less than a year 1 – 5 6 – 10 More than 10 |
47 97 35 28 |
22.71 46.86 16.92 13.52 |
|
What is your current position in the
organization? Owner Manager Employee |
13 40 154 |
6.28 19.32 74.4 |
|
How many employees does your organization
have (approximate number) Less than 5 5 – 10 11 – 50 51 – 100 More than 100 |
65 49 31 12 50 |
31.40 23.68 14.98 5.79 24.15 |
|
How old is the organization you work for
since its founding? Less than 5 years 5 – 10 11 – 15 16 – 20 More than 20 |
44 49 28 15 71 |
21.26 23.68 13.52 7.25 34.29 |
Results The Model Measurement
A confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used to confirm the validity of the overall model and to assess whether the measures for the latent variables were also reliable factors. This research used Cronbach’s alpha as a benchmark for the reliability assessment of each construct. DeVellis (2016) indicated that a Cronbach’s alpha (CA) over 0.7 is acceptable; the Cronbach’s alphas of CT, ITRM, ACT, GRS, and CRR were 0.948, 0.877, 0.898, 0.938, and 0.963, representing a high level of reliability for all constructs (Table 2). Furthermore, to evaluate internal reliability, composite reliability (CR) was used, with the outcomes proving that all CT, ITRM, ACT, GRS, and CRR values are exceeding the threshold of 0.70 (Table 2).
Table 2 A Confirmatory Factor Analysis Results (N = 207).
|
|
Number of Items |
Cronbach's Alpha |
R2 |
Composite Reliability |
Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|
9 |
0.948 |
0.152 |
0.950 |
0.706 |
|
|
ITRM |
4 |
0.877 |
|
0.882 |
0.730 |
|
ACT |
8 |
0.898 |
0.181 |
0.900 |
0.583 |
|
GRS |
6 |
0.938 |
|
0.938 |
0.764 |
|
CRR |
13 |
0.963 |
0.668 |
0.964 |
0.697 |
Table 2.
To assess the discriminant validity the Cross-loadings were conducted (Hair, Hult, Ringle, & Sarstedt, 2016) and confirmed that the discriminant validity was acceptable (Table 3). In addition, to evaluate convergent validity, the average variance extracted (AVE) was performed (Hair et al., 2016) Thus, the results confirmed that AVE values were well above 0.50.
Table 3
|
ACT |
CRR |
CT |
GRS |
ITRM |
|
|
ACT1 |
0.729 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT2 |
0.769 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT3 |
0.744 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT4 |
0.743 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT5 |
0.803 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT6 |
0.743 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT7 |
0.775 |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT8 |
0.799 |
|
|
|
|
|
CRR1 |
|
0.830 |
|
|
|
|
CRR2 |
|
0.879 |
|
|
|
|
CRR3 |
|
0.870 |
|
|
|
|
CRR4 |
|
0.732 |
|
|
|
|
CRR5 |
|
0.777 |
|
|
|
|
CRR6 |
|
0.810 |
|
|
|
|
CRR7 |
|
0.840 |
|
|
|
|
CRR8 |
|
0.835 |
|
|
|
|
CRR9 |
|
0.834 |
|
|
|
|
CRR10 |
|
0.871 |
|
|
|
|
CRR11 |
|
0.859 |
|
|
|
|
CRR12 |
|
0.871 |
|
|
|
|
CRR13 |
|
0.829 |
|
|
|
|
CT1 |
|
|
0.807 |
|
|
|
CT2 |
|
|
0.811 |
|
|
|
CT3 |
|
|
0.872 |
|
|
|
CT4 |
|
|
0.860 |
|
|
|
CT5 |
|
|
0.845 |
|
|
|
CT6 |
|
|
0.763 |
|
|
|
CT7 |
|
|
0.865 |
|
|
|
CT8 |
|
|
0.869 |
|
|
|
CT9 |
|
|
0.864 |
|
|
|
GRS1 |
|
|
|
0.837 |
|
|
GRS2 |
|
|
|
0.921 |
|
|
GRS3 |
|
|
|
0.889 |
|
|
GRS4 |
|
|
|
0.857 |
|
|
GRS5 |
|
|
|
0.870 |
|
|
GRS6 |
|
|
|
0.868 |
|
|
ITRM1 |
|
|
|
|
0.835 |
|
ITRM2 |
|
|
|
|
0.861 |
|
ITRM3 |
|
|
|
|
0.869 |
|
ITRM4 |
|
|
|
|
0.853 |
A path coefficient is utilized to assess the linkage between constructs in a structural model (Hair et al., 2016). The outcomes reveal that five paths with significant relationships (ACT -> CRR, GRS -> ACT, GRS -> CRR, GRS -> CT, and ITRM -> CRR) and one path with no significant relationship (CT -> CRR), (Table 4)
Discussion
The purpose of this study is to empirically assess SMBs' readiness towards cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia. Renaud and Ophoff (2021) stated that SMBs' lack of cyberattack readiness needs more attention from researchers. To address this gap, we examine the impact of government regulations and support, cyberattacks, information technology risk management, and awareness of cybersecurity-threat on MBS’s cyberattacks readiness. The results of this study proved that the model is acceptable. In addition, of 6 hypotheses, five hypotheses were supported.
To answer the first question, to what extent do cyberattacks impact the SMB's Readiness towards Cyberattacks, we examined the impact of cyberattacks on the SMB's readiness and found that cyberattacks have no negative impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack. A possible explanation is that the employees are unaware of the gravity of the cyberattack risk. For example, more than %70 of the participants are unaware of various cyberattacks such as social engineering, ransomware attacks, and Cross-site scripting. The findings are inconsistent with prior studies (Alharbi et al., 2021; Berry & Berry, 2018; Eilts, 2020). In addition, this research finding showed that the likelihood of the SMB being attacked is low. This indicates that the employees are not familiar with the types of cyberattacks which may put their organization at severe risk.
To answer the second question, to what extent does awareness of cyberattacks impact the SMB's readiness towards cyberattacks, we examined the impact of cyberattacks awareness and found that awareness of cyberattacks has a positive significant impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattack. The finding is consistent with prior studies (Eilts, 2020; Erendor & Yildirim, 2022). This finding indicates that a large number of SMBs are taking the proper plan to create effective cybersecurity awareness to attain adequate cybersecurity readiness toward cyberattacks. More than %60 of the participants have good knowledge regarding cyberattacks. A possible explanation is that the Saudi government employs different means to provide enough information regarding the cyberattacks and how SMBs should deal with them when the attack occurs. These means include cybersecurity campaigns, advertising campaigns, television, government agencies, and social media.
To answer the third question, to what extent does information technology risk management impact the SMB's readiness towards cyberattacks, we examined the impact of information technology risk management and found that it has a positive significant impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks. These findings support prior results by (Berry & Berry, 2018; Kiganda, 2022). The findings of this study revealed that the support of the top management has a significant effect on an organization's readiness toward cyberattack. More than 60 % of the participants stated that their organization conducts assessments for the impact of internal and external cyber threats and develops mitigation strategies to resolve potential problems that may result from cyberattacks on a regular basis. However, 30% of the participants indicated that their organizations do not conduct assessments for the likelihood of internal and external cyber threats on a regular basis which may put their organization's resources at severe risk. A possible explanation is that the organization owners do not have the resources nor the knowledge to make the right decisions. Berry and Berry (2018) argued that government institutions and private organizations should provide educational resources and antivirus tools to support small business owners who have limited funds.
To answer the fourth question, to what extent do government regulations and support impact the SMB's readiness towards cyberattacks, we examined the impact of government regulations and support and stated that government regulations & support have a positive impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks. The finding is consistent with the literature (Hasan et al., 2021; Kiganda, 2022). The findings show more than %80 of the participants believe that the government established appropriate regulations and provide outstanding support to help them update their current status regarding cyberattacks. In addition, the finding revealed the significance of government legislations and support in diminishing cyberattacks. Thus, SMBs must apply government legislations to enhance their ability to combat cyber incidents (Hasan et al., 2021). Furthermore, the findings stated that government regulations and support have a positive impact on SMBs' awareness of cyberattacks. Hence, government agencies may expand their cyberattack awareness campaigns to enhance their support for SMBs toward cyberattack readiness (Hasan et al., 2021).
Implications and Future Research
This study has several limitations. First, the population of this study was general SMB personnel regardless of the field of the organization. However, knowing the field of the organization may help in discovering the salient factors for each business. Future research may be considered the background of the employees and the field of the business. Second, the insignificant impact of cyberattacks on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks is noted, however, this finding cannot be generalized, because the participants were only from Saudi Arabia. Future research should assess the generalizability of the effect of cyberattacks on the SMB's readiness in different countries. Third, this study examined the factors impacting the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks to identify the salient factors. However, a longitudinal study may help in better understanding how well the SMB is prepared for cyberattacks. This may include three phases: measure the current cyberattacks readiness, then provide some of these SMBs with a cybersecurity awareness program, and finally, follow-up research to evaluate the impact of the awareness program on their preparedness towards cyberattacks.
This study enhances the body of knowledge in various ways. First, it presents a beneficial model that facilitates scholars to integrate different theories to recognize major factors influencing SMBs' readiness in the cyberattacks context. Second, the findings in this study can be used to facilitate future studies and improve the current understanding of how SMBs can be prepared to reduce the occurrence and effect of cyberattacks. Finally, practitioners may establish cybersecurity educational programs to enhance the awareness of cyberattacks that are focused on the vulnerabilities of SMBs.
Conclusions
SMBs are the most exposed to cyberattacks because they are less likely to have a reliable cybersecurity readiness strategy. In this study, a comprehensive model is utilized to combine various factors recognized from prior studies including, government regulations and support, cyberattacks, awareness of cybersecurity-threat, and information technology risk management impacting the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks. The results of this study proved that the model is acceptable. In addition, of 6 hypotheses, five hypotheses were supported. In addition, the findings showed that the factors, awareness of cyberattacks, information technology risk management, government regulations, and support have a significant positive impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks. However, this study indicated that cyberattacks have no significant negative impact on the SMB's readiness toward cyberattacks. A possible explanation is that the employees are not familiar with the types of cyberattacks which may put their organization at severe risk.
References
- Alharbi, F., Alsulami, M., Al-Solami, A., Al- Otaibi, Y., Al-Osimi, M., Al-Qanor, F., & Al-Otaibi, K. (2021). The impact of cybersecurity practices on cyberattack damage: The perspective of small enterprises in Saudi Arabia. Sensors, 21(20), 6901.
- Amankwah-Amoah, J., Khan, Z., Wood, G., & Knight, G. (2021). COVID-19 and digitalization: The great acceleration. Journal of Business Research, 136, 602-611.
- Bada, M., & Nurse, J. R. (2019). Developing cybersecurity education and awareness programs for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Information & Computer Security, 27(3), 393-410.
- Berry, C. T., & Berry, R. L. (2018). An initial assessment of small business risk management approaches for cyber security threats. International Journal of Business Continuity and Risk Management, 8(1), 1-10.
- CarÃas, J. F., Arrizabalaga, S., Labaka, L., & Hernantes, J. (2021). Cyber resilience self-assessment tool (cr-sat) for SMEs. IEEE Access, 9, 80741-80762.
- Chidukwani, A., Zander, S., & Koutsakis, P. (2022). A Survey on the Cyber Security of Small-to-Medium Businesses: Challenges, Research Focus, and Recommendations. IEEE Access, 10, 85701-85719.
- Chizanga, M. K., Agola, J., & Rodrigues, A. (2022). Factors Affecting Cyber Security Awareness in Combating Cyber Crime in Kenyan Public Universities. International Research Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology, 6(1), 54.
- Cybersecurity, C. I. (2018). Framework for improving critical infrastructure cybersecurity.
- DeVellis, R .F. 2016. Scale development: Theory and applications. Vol. 26. Los Angeles: Sage publications,
- rendor, M. E., & Yildirim, M. (2022). Cybersecurity awareness in online education: A case study analysis . IEEE Access, 10, 52319-52335.
- Estay, D. A. S., Sahay, R., Barfod, M. B., & Jensen, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of cyber-resilience assessment frameworks. Computers & Security, 97, 101996
- Gafni, R., & Pavel, T. (2019). The invisible hole of information on SMB's cybersecurity. Online Journal of Applied Knowledge Management (OJAKM), 7(1), 14-26.
- Gourisetti, S. N. G., Mix, S., Mylrea, M., Bonebrake, C., & Touhiduzzaman, M. (2019, April). Secure Design and Development Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (SD2-C2M2) Next- Generation Cyber Resilience by Design. In Proceedings of the Northwest Cybersecurity Symposium (1-9).
- Hair Jr, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage publications.
- Hasan, S., Ali, M., Kurnia, S., & Thurasamy, R. (2021). Evaluating the cyber security readiness of organizations and its influence on performance . Journal of Information Security and pplications, 58, 102726.
- Kiganda, M. (2022). An Assessment of the factors affecting cyber resilience in microfinance institutions in Kenya. (Doctoral dissertation, Strathmore University).
- McKinsey. (2020). How COVID-19 has pushed companies over the technology tipping point.
- Muncaster, P. (2020), Over 50,000 UK SMEs could collapse following cyber-attack.
- Ncubukezi, T., Mwansa, L., & Rocaries, F. (2020). A review of the current cyber hygiene in small and medium-sized businesses. In 2020 15th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST) (1-6). IEEE.
- Noparumpa, T., Ruangkanjanases, A., & Hariguna, T. (2021). Organization Benefit as an Outcome of Organizational Security Adoption: The Role of Cyber Security Readiness and Technology Readiness. Sustainability, 13(24), 13761.
- Paulsen, C., & Toth, P. (2016). Small business information security: The fundamentals. National Institute of Standards and Technology Interagency Report (NISTIR). 7621 Revision 1.
- Perozzo, H., Zaghloul, F., & Ravarini, A. (2022). CyberSecurity Readiness: A Model for SMEs based on the Socio- Technical Perspective. Complex Systems Informatics and Modeling Quarterly, (33), 53-66.
- Renaud, K., & Ophoff, J. (2021). A cyber situational awareness model to predict the implementation of cyber security controls and precautions by SMEs. Organizational Cybersecurity Journal: Practice, Process and People, 1(1), 24-46.
- Renaud, K., & Weir, G. R. (2016, August). Cybersecurity and the unbearability of uncertainty. In 2016 Cybersecurity and Cyberforensics Conference (CCC) (137- 143). IEEE.
- Rohn, E., Sabari, G., & Leshem, G. (2016). Explaining small business InfoSec posture using social theories. Information & Computer Security, 24(5), 534-556.
- Russell, A. L. 2014. Cyber blockades. Washington D.C: Georgetown University Press.
- Shaw, R. S., Chen, C. C., Harris, A. L., & Huang, H. J. (2009). The impact of information richness on information security awareness training effectiveness. Computers & Education, 52(1), 92-100.
- Sia, N. C., Hosseinian-Far, A., & Toe, T. T. (2021). Reasons behind poor cybersecurity readiness of Singapore’s small organizations: Reveal by case studies. In Cybersecurity, Privacy and Freedom Protection in the Connected World: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Global Security, Safety and Sustainability, London, (269-283).
- Syafrizal, M., Selamat, S. R., & Zakaria, N. A. (2020). Analysis of cybersecurity standard and framework components. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security, 12(3), 417-432.
- Teufel, S., Teufel, B., Aldabbas, M., & Nguyen, M. (2020). Cyber security canvas for SMEs. In Information and Cyber Security: 19th International Conference, ISSA 2020, Pretoria, South Africa, (20-33).
Cite this article
-
APA : Alarifi, S. H. (2023). Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia. Global Economics Review, VIII(I), 113-126. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2023(VIII-I).11
-
CHICAGO : Alarifi, Saleh H. 2023. "Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia." Global Economics Review, VIII (I): 113-126 doi: 10.31703/ger.2023(VIII-I).11
-
HARVARD : ALARIFI, S. H. 2023. Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia. Global Economics Review, VIII, 113-126.
-
MHRA : Alarifi, Saleh H. 2023. "Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia." Global Economics Review, VIII: 113-126
-
MLA : Alarifi, Saleh H. "Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia." Global Economics Review, VIII.I (2023): 113-126 Print.
-
OXFORD : Alarifi, Saleh H (2023), "Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia", Global Economics Review, VIII (I), 113-126
-
TURABIAN : Alarifi, Saleh H. "Small and Medium Businesses Readiness towards Cyberattacks in Saudi Arabia." Global Economics Review VIII, no. I (2023): 113-126. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2023(VIII-I).11

