Abstract:
The study interrogates the critical thresh hold limit of the external debt where the highly indebted economy becomes hanged and stagnant, pushes the economy towards. deeper poverty even below the poverty line. The other horizon aspect of relief in debt servicing is attributed to American and Russian war of 80s and war on the terror against Afghanistan after 9/11 forced the debt issuing agencies like Paris and Non-Paris Club and other lending aliened countries rescheduled and cut down debt servicing of Pakistan. This study examined the foreign debt effect on poverty by assuming dataset over the period from 1984 to 2017. The ARDL to co integration Approach was applied to get the findings that after debt thresh hold limit and debt overhang point, the foreign debt causes poverty in case of Pakistan. The other dimension if relief in debt servicing is provided this economic action depressed poverty.
Key Words:
ARDL Approach Poverty Reduction; External debt; Relief in Debt Servicing; FDI; Pakistan.
Introduction
The “Pauper” is Latin word applied on the people who have short supply of food, shelter, clean water, health facilities and international specific standard of living. The developing countries have been pushed in deeper poverty by excessive trend of external loans and debt servicing. More than 40 countries among107 developing countries have been declared . below the poverty line. Pakistan has exposed the poorest country among 43 countries (World Bank Report 2011). The burden of debt has pushed the country towards deeper poverty and depressed the economic growth. The debt above the minimum threshold limit has reached the country in Highly Indebted Poor Countries (World Bank report, 2011).
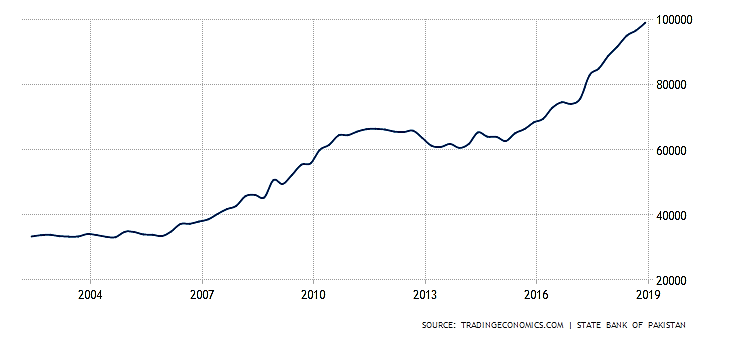
Figure 1: Source: State Bank of Pakistan
The figure also expresses the foreign loans digits of the country as:
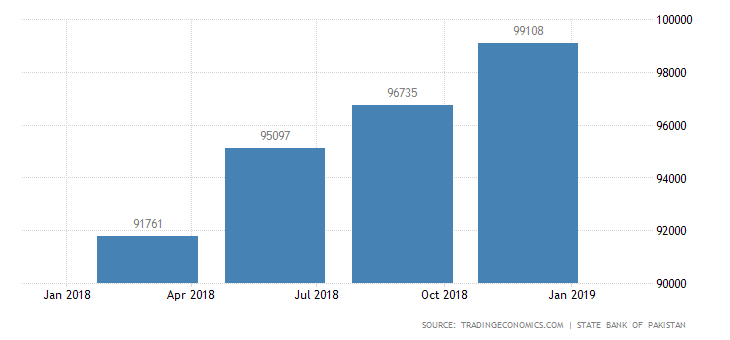
The history of foreign loans of Pakistan from 80’s has been shown in the given graph; it was at lower limit of 9.93 billion dollar but during 1990 the debt figures became double at $ 20 billion dollar. Further the burden of debt in 1999 was not stopped at this limit and climbed at $ 33.89 billion but in 2000 the govt. tried to push back to $ 32.78 billion but in 2010, it had reached dangerous stage point of $54.5 billion. . Afterwards next years, the situation of external debt became worse and worse than before. In current years the external debt has crossed threshold limit where the burden of loan has discouraged the economic growth and raised poverty. In 2018 the external had crossed $ 96 billion dollar and further surpassed the dangerous stage of minimum threshold limit $ 99 billion dollar (State Bank of Pakistan 2018). The last two years of external debt burden picture is portrayed by Diagram is as:
A well esteemed research conducted empirically, has exposed that the foreign debt generates the economic growth up to threshold limit but above minimum level its impact on economic growth becomes negative. A panel study on South Asian Countries revealed that Pakistan is the only country in which external debt has depressed economic growth and not reduced the poverty (Ajayi and Iyoha 1998), (Saddiqui and Malik 2002), (Uzochukw 2003).
Another approach was also examined to tackle the challenges of foreign debt and debt servicing, is utilization of government resources at optimal level. The govt. can boost up the economic growth poverty reduction by adopting cutting down unimportant and unproductive expenditures. Many financial supports like subsidies and protections can be removed to raise the resources and revenue of the government (Boopen et. al 2007).
The relief in debt servicing from debt lending institutions and countries can decrease foreign debt burden and raise the economic growth. This economic action of decreasing expenditures on debt can reduce poverty. American Russian war on their conflict about Afghanistan and in 9/11 war about terror against the land locked country Afghanistan, Pakistan supplied logistic and air support to America and her united countries. Against this support in war the America and her .Allies rescheduled debt service charges to cut down the burden of debt. Paris Club announces the relief in external debt about $ 21.3 billion dollar for 36 countries and further promised to issue concessional loans to 45 highly indebted poor countries (HIPC). Non –Paris Club contribution was $ 4.8 billion dollar in debt relief for HIPC. The burden of loan servicing of Pakistan has declined up to 2.3 % of gross familial production and further reduced up to 1.6 % gross familial production against these economic actions. The reduction in servicing as 11 % and further slipped down up to 23 % will be proved helpful in poverty alleviation (Patennio and Tan-Cuz 2007), (De and Yan Sun-Wang 2010).
The 30.5 million people of Pakistan are passing their lives not only at poverty line but they are spending their lives below the poverty line. In 2007 more than 30 million population of Pakistan was recorded that they were . below the poverty line in the world. In 2010 these statistics were reached up to 64 million (Pakistan Planning and Commission Report 2011).
The link between foreign debt, interest of debt and poverty has been controversial because some empirical studies reported that foreign loans and interest of loan servicing reduces poverty through economic growth. But the opposite view also exists that when the burden of external debt crosses minimum thresh hold limit, the effect of foreign debt and debt servicing becomes negative. The other view is revealed by researchers that external loans and service charges of loans depressed growth of the economy and raises the poverty due to misallocation and unproductive allocation of resources. So behind this background the empirical study becomes more important to reveal the link between poverty, foreign loans and loan servicing.
The Research Raises the Points are as:
1. How poverty is affected by the external debt in different phases of time period.
2. Measuring the response of loan interest and principal amount on poverty reduction.
3. To purpose the poverty reduction policy measures in the perspective of external debt and debt servicing measures which are effective for poverty alleviation
Literature Review on Foreign Debt Impact on Poverty
TahaZaghdoudi and AbdelazizHakimi (2017) reported the external debt effect the poverty by using the panel data from 2000 to 2015. The panel co-integration was operated on the data to conclude the link among foreign loan, poverty, home fixed investment and GDP per capita. The findings reflect that the burden of world debt in developing countries raises poverty.
JaveriaNaeem and Sadia Sherbaz (2016) interrogated the indebted effect on poverty by assuming the data set over the period 1973 through 2013. On time series data period the Johansen co integration econometric approach was applied to find out the conclusions that the internal and external debt both generates poverty in case of Pakistan.
Siddique and Selvanathan (2015) conducted research 40 indebted poor countries over the span 1970 to 2007. The econometric finding exposed that debt overhang issue of the economy is the major cause of internal and external discontinuous policies of the govt. Hence foreign debt increases poverty in indebted countries.
Ngerebo (2014) reported the effect of foreign debt on poverty explored in the Nigeria over the time series dataset to the span 1986 through 2012. The loan from external sources proved helpful in declining poverty derived empirical finding.
Atique and Malik (2012) reported interconnect between outer debt with the development of economy by using span of 1980 to 2010. The derived findings from dataset the study reported that foreign debt slip down the growth of economy.
Hassan and Butt (2008) interrogated the foreign debt effect on poverty through economic growth by applying on data over the period of 31 years (1975-2005) of Pakistan. The autoregressive distributive lag model was applied to get the empirical findings of this study. In short run the debt has no impact on poverty while misallocation of resources in the long run burden of debt depressed growth of the economy.
Boopen et. al (2007) examined foreign debt association with growth of output of Mauritius economy by using the dataset span over the period of 1960 to 2004. The ARDL method of co integration was applied and concluded that foreign debt did not improve welfare of the poor and the growth of output.
Uzochukw (2003) investigated external debt effect on poverty in Nigeria over the dataset for the 31 years (1970-2002). The study revealed that the external debt raised poverty in the country by adopting the capita income approach.
Saddiqui and Malik (2002) analyzed the foreign debt impact on the growth rate of GDP. Panel empirical estimation was launched on the dataset to reveal the results. The research has reported that the foreign aid encourages the growth up to certain level or thresh hold point but above the thresh hold limit, it becomes burden on economy and increases poverty trough depressed economic growth.
Stiglitz (2000) analyzed the crowding out effect of foreign debt as a result that the international interest rate and debt servicing increases which discourages the investment and ultimately affects the economic growth negatively. The wages are reduced and purchasing power also decreases caused deeper poverty.
Ajayi and Iyoha (1998) interrogated empirical relationship between foreign debt and poverty by assuming the data from 1990 to 1997.Simultaneous econometric approach was applied to get the core finding of this research work. The foreign loan burden discourages the economic growth of the highly indebted poor countries.
Literature Review on Relief in Debt Servicing Effect on Poverty
Naeem Akram (2016) reported the public debt, foreign loans and servicing of debt effect
on poverty of Countries associated with South Asian region by taking span over the dataset from 1975 to 2010. Panel data estimation method was operated to conclude research finding that external loan discouraged the economic growth while the external loans and loan servicing has good effect on rich country and bad impact on poor countries.
Oyedele, et al. (2013) reported that the impact of outer debt and loans servicing on the poverty of Nigeria by adopting the data set span over 1980 2010. Co-integration approach OLS technique of econometric was operated to estimate the results that debt has raised the poverty in Nigeria.
Boboye, Michael (2012) examined the empirical impact of foreign loan service, rate of interest, foreign debt and their effect on national income by assuming the dataset of 27 years. OLS approach was operated to find the conclusion of regression and reported that relief in loan servicing generates the national income of the economy.
Abubaker and Hassan (2008) discussed the empirical effect of foreign debt servicing on the Malaysian development of the economy. In this study interrogated Malaysian economic growth was not adversely affected with burden of foreign loan interest rather debt encouraged agents which revived the growth.
Patennio and Tan-Cuz (2007) reported the empirical research of Philippine to get the affiliation between loan service and poverty through development of economy by taking data for the span over 1981 to 2005. By applying the econometric method to conclude the empirical results that the burden of debt servicing had not been challenged and threatened for poverty and economic growth.
Klementset.al (2005) examined the econometric study on debt servicing and economic growth and reported that if relief in foreign interest rate as 6 percent of Gross Domestic Production increases the government investment up to 25 percent. As a result of increase in investment generates the economic growth by 0.2 from its standing point.
Gupta, Clements, Bhattacharya, Nguyen (3003) focused on debt servicing, gross domestic investment, .external debt, population growth rate and change in the rate of income by assuming dataset over the period of 55 years under developing economies data from 1970. .. The study concluded that relief in loan servicing raises the growth rate of economy and growth rate of incomes.
Kemal (2001) conducted research on debt servicing multidimensional role on poverty through economic growth of Pakistan. The research, resulted the burden of service loan, was more than other South Asian Countries but Pakistan has the capacity of paying back the charges in the form of servicing. Hence the debt and relief in debt servicing reduces the poverty and causes the economic development.
Specification of the Model and Data Source
Log HC = ?0 + ?1 log TD+ ?3 log TDS + ?4 log RGGR + ?5 log INF+ ?6 log PGR+ ?7 log FDI + ui
HR = The Head Count Ratio is used as proxy of poverty or miser.
ED = Foreign / External Debt / loan as a % of GNP
RDS = Relief in foreign interest or loan servicing as a % of GNP for debt relief.
RGDPGR = Real Gross Domestic Production Growth Rate
INF = Rate of Inflation
GRP = Population Growth Rate
FI = Foreign Investment
The study has adopted the dataset collected by United Nation Development Program World Develop Indicator (WDI) and State Bank of Pakistan for the span over 1984-2017.
The Test of Unit Root
The test of unit root that the application of ARDL approaches to co-integration is not necessary condition for the getting stationary order of variables. But it is just sufficient condition to use the test for stationary order of the data that, none of the variables should. exist at 2nd order. In the presence of second order of the variable the ARDL method totally fails in estimating the results (Pesaran and Pesaran (1997).
Table 1. The test of Unit Root
|
Variables |
ADF Test Statistics
(at level) |
ADF Test Statistics
(at Ist Difference) |
Stationary Status |
|
LHC |
-2.315 |
-4.732* |
I (1) |
|
LED |
-0.351 |
-4.245** |
I (1) |
|
LRDS |
-0.421 |
-7.383* |
I (1) |
|
LGDPGR |
-4.235** |
-2.315 |
I (0) |
|
LINF |
-3.254** |
-6.235 |
I (0) |
|
LPGR |
-3.845** |
1.235 |
I (0) |
|
LFI |
-3291 |
-6.235* |
I (1) |
Note: * and ** Showing the Significance Level at 1% and 5% Respectively
Co Integration
The correction of error system is used to investigate the association between variables outer debt, relief in real GDP growth rate, debt servicing, inflation, growth rate of population and foreign investment in both long run and short run (Pesaran and Pesaran1997) and (Pesaran and Shin 1999) below as:
?log?HR?_t=?_0+?_(i=1)^N???_1 ?log? HR?_(t-i) ?+?_(i=0)^N???_2 ?log ?ED?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_3 ?log? RDS?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_4 ?log? GRP?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_5 ??log INF?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_6 ?logRG?DPGR?_(t-i)+?_(i=0)^N???_7 ?log? FI?_(t-i) ?+?_1 log? HR?_(t-1) ?+??_2 log? ED?_(t-1)+?_3 log? RDS?_(t-1) ?+?_4 log? RGDPGR?_(t-1)+?_5 ?log INF?_(t-1)+??_6 ?log GRP?_(t-1)+?_7 ?log FI?_(t-1)+?_t ?
………………………….. (A)
The bound test of ARDL to co integration which expresses the association of long run between the variables exists. The unrestricted error adjustment mechanism coefficient represents the picture of lag coefficients in short run.
?log?HR?_t=?_0+?_(i=1)^N???_1 ?log?HR?_(t-i) ?+?_(i=0)^N???_2 ?log?ED?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_3 ?log?RDS?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_4 ?log?GRP?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N???_5 ??log INF?_(t-i)+? ?_(i=0)^N??_6 log RGDP?GR?_(t-i)+?_(i=0)^N???_7 ?log?FI?_(t-i) ?+?_t
……………………. (B)
F-test or bound test is applied on the combined significance of the sum of all lagged variables to co-integration. The lag of variables of the level of each variable is added to the equation (B) to create error correction mechanism in this equation, now calculate variable Addition Test.
Table 2. Explanation of Bound Test
|
F-Calculated |
95% Confidence
Interval |
90% Confidence
Interval |
||
|
7.314 |
Lower Limit |
Upper Limit |
Lower Limit |
Upper Limit |
|
3.412 |
4.524 |
2.642 |
4.182 |
|
Source: Author Own
Estimation
The calculated value of bound test is 7.314 has crossed from lower value3.412 and upper value 4.524 at 95% confidence interval and below limit value 2.642 and higher limit value4.182 at 90 % confidence interval which favors alternative hypothesis that long run link persist among the variables and confirms the presence of long run relationship. Here HC is dependent variables while the TD, TDS, GDPGR, INF, PGR and FDI are co integrated.
Table 3 Long Run Estimation of the Model
|
Variables |
Coefficients |
T-Ratios |
P-Values |
|
LED |
.425 |
3.771 |
(.001) |
|
LRDS |
-.235 |
-4.270.87 |
(.000) |
|
LRGDPGR |
-.248 |
-3.557 |
(.003) |
|
LINF |
.132 |
2.720 |
(.012) |
|
LGRP |
-.325 |
-2.494 |
(.020) |
|
LFI |
-.172 |
-3.781 |
(.000) |
Source: Author Own Estimation
The long run findings of the research
exposed that when foreign debt surpasses the boundaries of minimum thresh hold
limit it raises the poverty a country. As 1 % increases in foreign debt raises
the poverty by 42% and the other important finding is that if relief is given
in the form of reschedule of debt and debt servicing reduces the poverty of
domestic country by 23.5%. The other control variables RGDPGR, growth rate
population (GRP) and foreign direct investment (FI) reduces the poorness while
the inflation generates the poverty in case of Pakistan. All coefficients are
consistent at 1% and 5 %.
Table 4 Dynamic ARDL Model Based on Schwartz Lag Estimation when Log HCR is Dependent Variable
|
Variables |
Coefficients |
T-Ratios |
P-Values |
|
LHR (-1) |
.184 |
2.109 |
(.048) |
|
LED |
.240 |
3.131 |
(.006) |
|
LRDS |
-.237 |
3.263 |
(.004) |
|
LRDS (-1) |
-.102 |
2.35 |
(.030 |
|
RGDPGR |
-.124 |
2.355 |
(.030) |
|
RGDGR (-1) |
-.054 |
1.679 |
(.10) |
|
LINF |
.104 |
2.503 |
(.022) |
|
LGRP |
-.243 |
1.502 |
(.206) |
|
LFI |
-.028 |
2.503 |
(.022) |
Source: Author Own Estimation
The lag variables are operated
at first; lag explains the results of short period. As one % increases in ED
the poverty raises by 24 %. The other variable 1% rise in relief in debt
servicing reduces the poverty by 23 %. The 1% increase in lag value relief in
debt servicing declines the poverty by 10.2% and real GDP growth rate depressed
the poverty by 12.4%. Inflation rise causes increase in poverty by 10.4%. The
growth rate of population also raises the poverty by 24.3 % while the role FI
decreases poverty by 2%. The ED affects the poverty positively but if relief is
given in the form of rescheduling or debt reduction declines poverty in case of
Pakistan.
Table 5 Error Correction Model Explanation
|
Variables |
Coefficients |
T-Ratios |
P-Values |
|
dLED |
.285 |
3.565 |
(.002) |
|
dLRDS |
-.134 |
-3.381 |
(.003) |
|
dLRGDPGR |
-.342 |
-2.162 |
(.042) |
|
dLINF |
.124 |
3.13 |
(.005) |
|
dLGRP |
-.284 |
-2.812 |
(.010) |
|
DLFI |
-.042 |
-2.8813 |
(.008) |
|
Ecm (-1) |
-.564 |
-4.40 |
(.000) |
Source: Author Own Estimation
The table explains the term error
adjustment coefficient which portrayed the short period findings. A rise 1 % in
total debt increases the poverty by 28 %. As 1% relief in debt servicing
reduces the poverty respectively by 13% and 1% rise in population growth rate
raises poverty by 34.2 % and foreign direct investment declines the poverty by 4 %. 1% increase in real GDP
growth rate causes the adverse effect in poverty by one percent and one percent
rise in inflation increases misery of the people by 12.4. The magnitude of
coefficient associated with negative sign ecm (-1), the sign of highly
significance of model. The adjustment coefficient value is -.564 reflects the
convergence to towards the equilibrium and explains long run link among
parameters present in empirical analysis. The error correction coefficient
value is
.564
reflects the self-correction per year showed the relationship among variables
in the long run. The adjustment term ecm (-1) explains 56.4 % absence of
equilibrium in the previous year will correct disequilibrium in the present
year. This adjustment value .564 suggests that 56.4 % is adjustment coefficient
rectifying the equilibrium in the coming year.
Table 6 Structure of Good Fit Model
|
R2 |
0.83 |
|
Adjusted
R2 |
.861 |
|
D.W-Statistics |
2.024 |
|
F
(6,21) |
17.621 |
Source: Author Own Estimation
The R2value reflects that 0.83 % change in the poverty is reflection of explanatory variables and other variation in the model is the result of stochastic term. The more magnitude of R2 reveal the model is good fit while adjusted R2, represents the good fitness of the model associated with degree of freedom.
Table 7 Diagnostic Test
|
Problem |
LM-Version
(P.V) |
F-Version (P.V) |
|
Serial Correlation |
(.582) |
(.824703) |
|
Functional Form |
(.164) |
(.425309) |
|
Normality |
(.642) |
Not applicable |
|
Hetroscedasticity |
(.725) |
(.722) |
Source: Author Own Estimation
The p-value of the LM and F-Version is above10 % confirms the hat there is no serial correlation or the problem of Hetroscedasticity. Correct Functional form is attributed to Ramsey Reset test and Lagrange Multiplier test is used for autocorrelation. Here OLS assumptions of econometric technique are not violated. Hence the model is efficient and consistent for prediction.


The graphs of Cumulative Sum of Recursive Residual CUSUM and CUSUM sum of
square are in between 5 % critical bound limit. The sign of structural stability of the model in both periods is without structural gaps in the estimated model. The stability test is attributed to Pesaran and Pesran (1977) to check the structural breaks in the model.
Conclusion
This paper reported the opposite results from previous study that log ED, log RDS, log RGDPGR, log INF, log GRP and log FI are statistically significant long run relationship with log HR. The econometric conclusions of the research are that the external debt has crossed the minimum thresh hold limit of debt hence raising poverty in the case of Pakistan. The results of the former researches on the same topic .are not matched to the result of this empirical study. The most important finding of the research is that if the foreign debt lending institutions are agreed to cut down the debt servicing burden or reschedule the debt. This economic action will encourage the economic growth and reduce the poverty of the domestic country in long run. Further the study .concludes that the real GDP growth, Population Growth rate and Foreign Investment depressed the poverty in long run and these variables .empirically rejects null hypothesis at 1% and 5%level. The model strongly advocates error adjustment coefficient associated with negative sign. The ecm (-1) portraits the picture of short runs co integration of variables. The negative value ecm (-1) coefficient shows convergent of the model towards the equilibrium. The magnitude of the coefficient adjustment recommends that 56.4 % disequilibrium in poverty in current year will push the model towards equilibrium in the next year. The graphs of CUSM and CUSM sum of square are in between bound limit at 5% significance level confirm stability of the model critical without structural breaks.
References
- Abu Bakar, N. A. and Hassan, S., (2008),
- Ajayi, Boboyye, L. and Michael, O. (2012)
- Ajayi, S.I. and M. Iyoha (1998), Debt overhang and Debt Forgiveness: The Case of the Severely Indebted LowIncome Countries of Sub-Saharan Africa, Journal of Economic Management. Vol. 5, No.1 Applied Economics
- Amakom (2003), Nigeria Public Debt and Economic Growth: An empirical Assessment Uzochwkwus Nigeria.
- Atique, R. and Malik, K. (2012)
- Boopen, S., Kesseven, P. and Ramesh, D., (2007),
- Clements, B., Bhattacharya, R. and Nguyen, T., (2005),
- Enugu, Siddiqui, R. and A. Malik (2002)
- Gupta, Sanjeev, Benedict Clements, Alexander Pivovarsky, and Erwin R. Tiongson, 2003,
- Hasan, A. and Butt, S., (2008),
- Kemal.A.R (2001), Debt Accumulation and Its Implications for Growth and Poverty: The Pakistan Development Review, 40(4) Parts.
- Muhtar (2004): Weak External Demand for Philippine Export is Dampening Growth. Malik 677- 688.
- Naeem, J. and Sherbaz, S., (2016). Indebtedness and Poverty: The Case of Pakistan, The Pakistan Development Review 55:4 Part II, pp. 823-835.
- Ngerebo, T. A. (2014) Domestic Debt and Poverty in Nigeria: An Empirical Time Series Investigation, European Journal of Accounting Auditing and Finance Research 2:5, 33-47.
- Oyedele, S. O., A. A. Emerah, and S. Ogege (2013) External Debt, Debt Servicing and Poverty Reduction in Nigeria: An Empirical Analysis. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development 4:19. Rogoff, K. (1992) Dealing with Developing Country Debt in 1990s. World Economy 15, 475-486.
- Patenio, J. A. S. and. Tan-Cruz, A., (2007),
- Siddique, A., Selvanathan, S. (2015). The impact of external debt on economic growth: empirical evidence from highly indebted poor countries (31 p.) (Discussion paper). University of Western Australia. Business School Economics.
- Siddiqui, R. and Uzochwkwus, Amakom (2003), Nigeria Public Debt and Economic Growth: An empirical Assessment of Effects on Poverty. Africa Institute for Applied Economics Enugu Nigeria
- Stiglitz, J.E. (2000), Economic of the Public Sector, New York and London. W.W. Norton and Company of Effects on Poverty, Economics Enugu Economics, A., (2002),
- Zaghdoudi, Z. and Abdelaziz Hakimi, A., (2017). Does external debt-poverty relationship confirm the debt overhang hypothesis for developing counties? Economics Bulletin 37(2):653-665.
Cite this article
-
APA : Shahid, M., Shah, M., & Sadiqa, B. A. (2019). Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy. Global Economics Review, IV(IV), 23-34. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2019(IV-IV).03
-
CHICAGO : Shahid, Muhammad, Mahmood Shah, and Bibi Aisha Sadiqa. 2019. "Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy." Global Economics Review, IV (IV): 23-34 doi: 10.31703/ger.2019(IV-IV).03
-
HARVARD : SHAHID, M., SHAH, M. & SADIQA, B. A. 2019. Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy. Global Economics Review, IV, 23-34.
-
MHRA : Shahid, Muhammad, Mahmood Shah, and Bibi Aisha Sadiqa. 2019. "Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy." Global Economics Review, IV: 23-34
-
MLA : Shahid, Muhammad, Mahmood Shah, and Bibi Aisha Sadiqa. "Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy." Global Economics Review, IV.IV (2019): 23-34 Print.
-
OXFORD : Shahid, Muhammad, Shah, Mahmood, and Sadiqa, Bibi Aisha (2019), "Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy", Global Economics Review, IV (IV), 23-34
-
TURABIAN : Shahid, Muhammad, Mahmood Shah, and Bibi Aisha Sadiqa. "Foreign Debt and Debt Servicing Relief Effect Implications in Pakistan: A Poverty Reduction Strategy." Global Economics Review IV, no. IV (2019): 23-34. https://doi.org/10.31703/ger.2019(IV-IV).03
